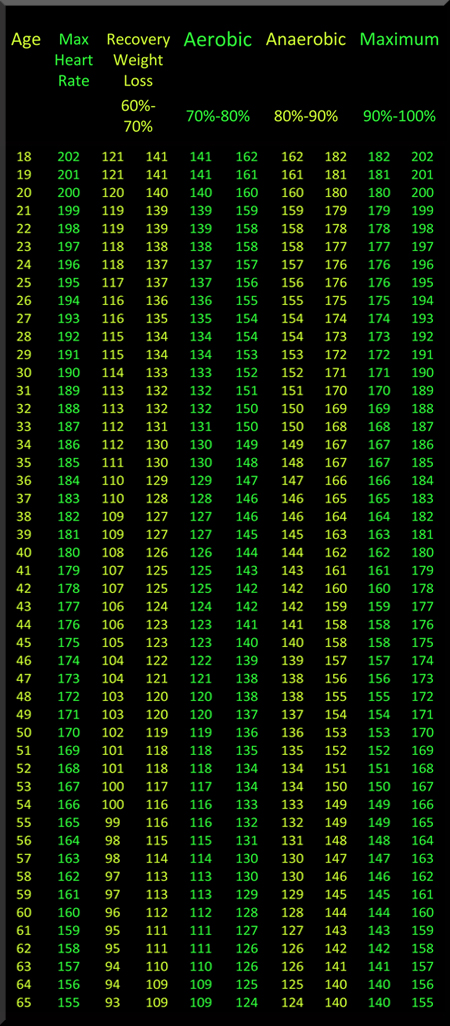
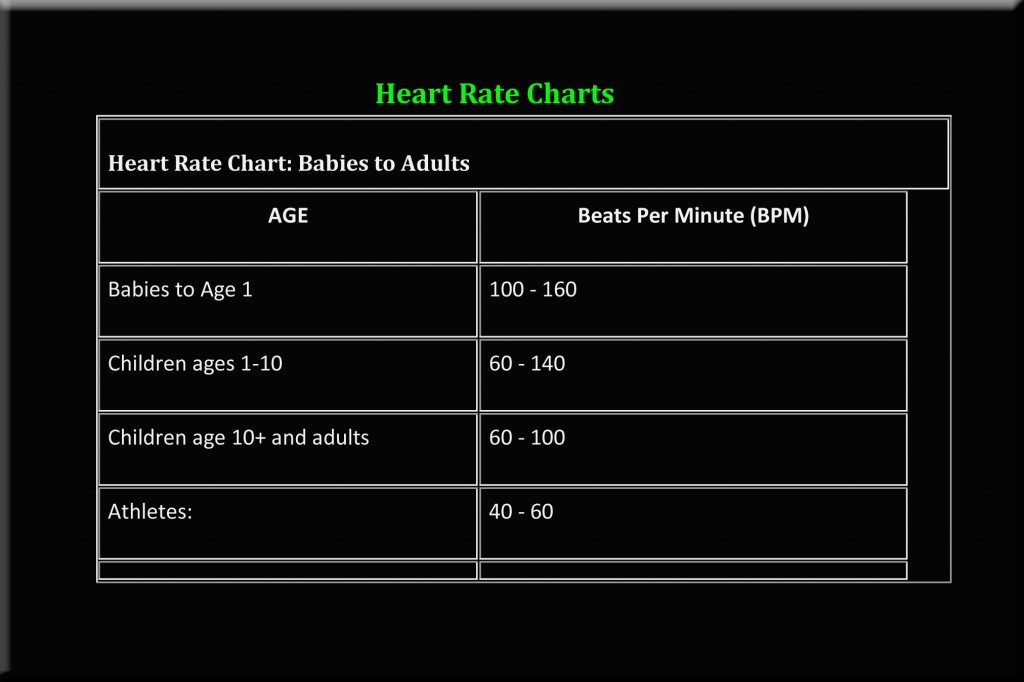
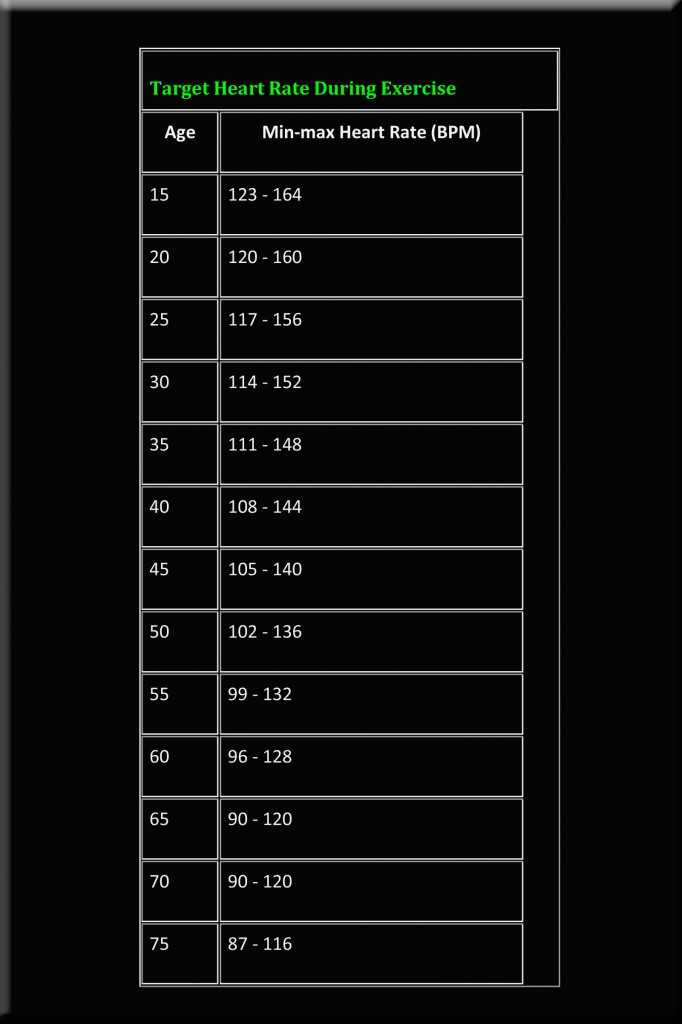
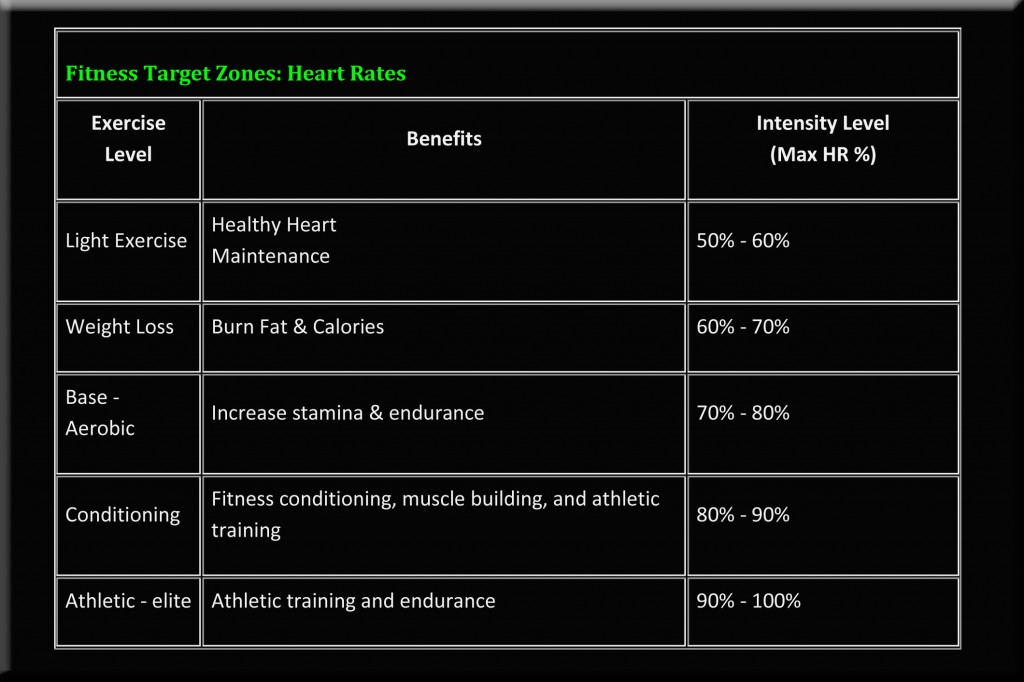
Pre & Post Workout Cocktails
Wed ,18/05/2011In order to prep my body for a peak performance during a demanding early AM workout regimen, I will wake up and go directly to the kitchen for my pre-workout “cocktail” (protein shake). The rule of 25 In 25 (25 g. of protein within 25 minutes of waking up) is a way of life for me. When we wake in the mornings, our bodies have been on an 8-12 hour fast and as we wake our body begins to draw on an already empty fuel tank. This is a critical time of the day in that we must give our body the much needed proteins or it will produce cortisol and slip into a catabolic state. A protein shake or meal replacement is a perfect remedy for this. Below is an example of my morning “cocktail” regimen.
Pre-Workout Shake Dosage
Whey protein Isolate 35 g.
Mixed with 10 ounces 1% milk
BCAA’s 5 g.
Glutimine 5 g.
L-Arginine 1 ½ g.
Beta-Alanine 1 g.
Flaxseed (ground) 10 g.
Blue Berries (frozen) 35g. (about ¼ cup)
30 minutes Prior to My Workout
I will drink a pre-workout nitric oxide formula. I start the timer immediately upon drinking this one, because my body feels like it is ready to kick into high gear within 5-10 of consumption. Allowing 30 minutes for the ingredients to take full effect on the body is a must, not to mention If I step on the treadmill to soon, I will get a bit of a side ache from the fluid:
SuperPump Max 48 g.
Mixed in 12 ounces of water
1-1 ½ Hour into Workout
In the later portion of my workout, I will begin to drink my creatine cocktail that was already prepared in a small shaker bottle:
VoluGro (Creatine Monohydrate) 38 g.
Mixed in 10 ounces water
Immediately after I hae finished with my workout, I will return to the kitchen for my post-workout cocktail. This is another critical window where the body is demanding a fast acting protein and carbohydrate intake. Your body is depleted of energy source and your muscles will quickly absorb the carbs you ingest. Think of your body as having an empty fuel tank and your motor is running at a high RPM, even though you have finished your workout, you metabolism is charged to run.
Post-Workout Shake
High Protein Anabolic Gainer 75 g.
Mixed in 10 ounces of 1% milk
BCAA’s 5 g.
Glutimine 5 g.
L-Arginine 1 ½ g.
Beta-Alanine 1 g.
Blue Berries (frozen) 35g. (About ¼ cup)
As a general rule, I will repeat these two cocktails one more time each through the day, generally i will drink another whey protein mid to late afternoon and the high protein with a high carbohydrate complex late evening, prior to bedtime. This I will do along with a healthy diet of 3-6 square meals. Remember, protein builds muscle, carbohydrates fuel the muscle, and that tomorrow’s performance will be based on today’s loading of adequate nutrition.
While I do not recommend that everyone run out and break the bank buying all the components for these yummy cocktails. I do however recommend that you apply the “25 grams of protein within 25 minutes” rule (25 In 25), a healthy diet, and a minimum of 2 ½ -3 hours of working out a week. This is an excellent starting point to assess your body’s condition and build upon your short and long term fitness goals.
Consult with your Doctor about the application and usage of these supplements and cardio activities.